Summary of The First Half of Semester
- Rhenald Ariendra

- Apr 6, 2020
- 5 min read
LINKED LIST
Definition of Linked List
Linked list is sequence of data that are connected through a link. Linked list the second most used data structure after array. Linked list contains of head that store the first address of the link, node that used to store the data you want to store and a link to the next data, and in the last data the link should be NULL.
There are 3 types of linked list :
1. Single linked list
2. Double linked list
3. Circular linked list
Basic Operator in a Linked List
There are some basic operators that you can use in a linked list :
1. Insert
Basically insert is an operator that you use to insert a variable.
2. Delete
This operator let you delete data that you want to delete.
3. Display
This operator will display all the linked list that you already store.
4. Search
This operator will let you search data and display only the data that you want to search.
Single Linked List
Single linked list is a list that only connected to the next link, so we can only navigate it forward. Below is an illustration of single linked list.
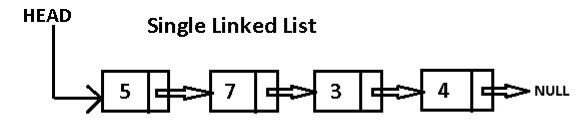
And here is how to create a single linked list in C.

Here is some code of to insert and delete element of single linked list.

Notes : root is the same as head in the illustration above.

Notes : the code above is to delete a data in a certain position (the position will start with index of 0 same with an array).
Double Linked List
Double linked list is a list of data that link to the next and previous data if present. So it is different than single linked list we can navigate it forward and backward. Below is an illustration of double linked list.

And here is how to create a double linked list in C.

Below are some codes to delete and insert data of a double linked list,


Circular Linked List
Circular linked list is a linked list where the last link contains the first element of the first element and the first link also has the element of the last link. Circular linked list can based on single linked list and double linked list. Below are illustrations of circular single linked list and circular double linked list.


HASHING & BINARY TREE
HASHING
Hashing is a technique used for storing and retrieving keys in a rapid manner. Also defined as a concept of distributing keys in an array called hash table using a predetermined function called hash function. Hashing is used to index and retrieve items in a database because it is faster to find item using shorter hashed key than to find it using the original value. For example :
1. In universities, each student is assigned a unique roll number that can be used to retrieve information about them.
2. In libraries, each book is assigned a unique number that can be used to determine information about the book, such as its exact position in the library or the users it has been issued to etc.
Hashing is implemented in two steps:
1. An element is converted into an integer by using a hash function. This element can be used as an index to store the original element, which falls into the hash table.
2. The element is stored in the hash table where it can be quickly retrieved using hashed key.
- hash = hashfunc(key)
- index = hash % array_size

1. HASH FUNCTION
A hash function is any function that can be used to map a data set of an arbitrary size to a data set of a fixed size, which falls into the hash table. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, hash sums, or simply hashes. To achieve a good hashing mechanism, you should need :
1. Easy to compute.
2. provide a uniform distribution across the hash table and should not result in clustering.
There are many ways to hash a string into a key. The following are some of the important methods for constructing hash functions.
• Mid-square
• Division (most common)
• Folding
• Digit Extraction
• Rotating Hash
2. HASH TABLE
Hash table is a table (array) where we store the original string. Index of the table is the hashed key while the value is the original string. The size of hash table is usually several orders of magnitude lower than the total number of possible string, so several string might have a same hashed-key.
TREE & BINARY TREE
A tree is a non-linear data structure that represents the hierarchical relationships among the data objects. Some of the tree relations can be observed in directory structures or organizational hierarchies. Commonly used terminologies for tree:
1. Root: Top node in a tree
2. Child: Nodes that are next to each other and connected downwards
3. Parent: Converse notion of child
4. Siblings: Nodes with the same parent
5. Descendant: Node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child
6. Ancestor: Node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent.
7. Leaf: Node with no children
8. Internal node: Node with at least one child
9. External node: Node with no children
There are also 4 types of binary tree :
1. Perfect Binary Tree : binary tree in which every level are at the same depth.

2. Complete Binary Tree : binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible. A perfect binary tree is a complete binary tree.

3. Skewed Binary Tree : binary tree in which each node has at most one child.

4. Balanced Binary Tree : binary tree in which no leaf is much farther away from the root than any other leaf (different balancing scheme allows different definitions of “much farther”).
And here is an example of single linked list to make some kind of market.
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> struct node { char name[100]; int quantity; int price; struct node *left; struct node *right; }; struct node* root = NULL; struct node* getnode(){ return (struct node *)malloc( sizeof(struct node)); } // void viewItem(){ if(root==NULL){ printf("There is no item\n\n"); return ; } printf("Item List :\n"); int idx=1; struct node*p=root; do{ printf("%d. %s Quantity = %d || Price(per item) = %d\n", idx, p->name, p->quantity, p->price); p = p->right; idx++; }while(p!=NULL); printf("\n"); } void sortedInsert(struct node** head, struct node* nodeBaru){ struct node* curr; if (*head == NULL) *head = nodeBaru; else if (strcmp((*head)->name,nodeBaru->name)>0) { nodeBaru->right = *head; nodeBaru->right->left = nodeBaru; *head = nodeBaru; } else { curr = *head; while (curr->right != NULL && strcmp(curr->right->name,nodeBaru->name)<0) curr= curr->right; nodeBaru->right = curr->right; if (curr->right != NULL) nodeBaru->right->left = nodeBaru; curr->right = nodeBaru; nodeBaru->left = curr; } } void insertionSort(struct node** head){ struct node* sorted = NULL; struct node* curr = *head; while (curr != NULL) { struct node* right = curr->right; curr->left = curr->right = NULL; sortedInsert(&sorted, curr); curr = right; } *head = sorted; } // // void addItem(){ char str[100]; int harga; int banyak; struct node* temp = getnode(); do{ printf("Input Item Name : "); scanf("%[^\n]", &str); getchar(); }while(strlen(str)<3||strlen(str)>15); if(str[0]>='a'&&str[0]<='z'){ str[0] -= 32; } strcpy(temp->name, str); printf("Input Item Quantity : "); scanf("%d", &banyak); temp->quantity = banyak; harga = rand()%50 + 1; // harga = (rand() % (50 - 1 + 1)) + 1; harga *= 1000; temp->price = harga; temp->left=NULL; temp->right=NULL; if(root==NULL){ root = temp; } else{ struct node *p = root; while(p->right!=NULL){ p = p->right; } p->right = temp; temp->left = p; } printf("--- Item Successfully Added ---\n"); printf("\n"); } // // int validasiExist(char str[]){ if(root==NULL){ return 1; } struct node *p = root; do{ if(strcmpi(p->name,str)==0){ return 0; break; } p = p->right; }while(p!=NULL); return 1; //valid 1 invalid 0 } void updateItem(){ char str[100]; int flag = 0; if(root==NULL){ printf("There is no item yet\n"); return ; } char a[10]; do{ printf("Input Item Name to Update : "); scanf("%[^\n]", &str); if(validasiExist(str)==1){ do{ printf("There is no item with that name\nDo you wish to enter another item [yes/no] : "); scanf("%s", &a); getchar(); if(strcmpi(a,"yes")==0){ continue; } else{ printf("\n"); return ; } }while(strcmpi(a,"yes")!=0&&strcmpi(a,"no")!=0); } }while(validasiExist(str)==1); struct node*p=root; while(p->right!=NULL){ if(strcmp(p->name,str)==0){ break; } p = p->right; } int banyak; printf("Input New Quantity : "); scanf("%d", &banyak); p->quantity = banyak; printf("--- Item Successfully Updated ---\n"); printf("\n"); } // // int length(){ int count=0; struct node *temp; temp = root; while(temp!=NULL){ count++; temp = temp->right; } return count; } void deleteItem(){ if(root==NULL){ printf("There is no item yet\n"); return ; } int flag = 0; struct node*p=root; char str[100]; char a[10]; do{ printf("Input Item Name to Delete : "); scanf("%[^\n]", &str); if(validasiExist(str)!=0){ do{ printf("There is no item with that name\nDo you wish to enter another item [yes/no] : "); scanf("%s", &a); getchar(); if(strcmpi(a,"yes")==0){ continue; } else{ printf("\n"); return ; } }while(strcmpi(a,"yes")!=0&&strcmpi(a,"no")!=0); } }while(validasiExist(str)!=0); int count = 1; do{ if(strcmpi(p->name, str)==0){ break; } count++; p = p->right; }while(p!=NULL); printf("Deleted Item : %s\n", p->name); struct node*temp; if(count==1){ temp = root; root = temp->right; temp->right = NULL; free(temp); } else if(count==length()){ struct node*u=p->left; u->right = NULL; p->left = NULL; free(p); } else{ struct node *next = p -> right; struct node *prev = p ->left; prev -> right = next; next -> left = prev; p -> right = NULL; p -> left = NULL; free(p); } printf("\n"); } // // long long int checkout(){ long long int angka = 0; struct node*p=root; do{ angka+=(p->quantity*p->price); p=p->right; }while(p!=NULL); return angka; } void printMenu(){ printf("DREAMERS MARKET\n"); printf("==================\n"); printf("1. View Item\n2. Add New Item\n3. Update Item Quantity\n4. Delete Item\n5. Checkout\n6. Exit\nChoice : "); } int main(){ int choice; do{ printMenu(); scanf("%d", &choice); getchar(); switch (choice) { case 1: insertionSort(&root); viewItem(); break; case 2: addItem(); break; case 3: updateItem(); break; case 4: deleteItem(); break; case 5: insertionSort(&root); viewItem(); if(root!=NULL){ printf("Total Price = %lld\n", checkout()); printf("BUT!\nIt's Free Now, Kindness is Free\n\n"); } break; default: break; } }while(choice!=6); return 0; }
References :
1. Power point of linked list (I) & linked list (II)
5. Binusmaya powerpoint hashing 7 binary tree
For the Image Sources :
1. First image

Comments